Search Results for: primary structure
Primary structure
Definition noun (biochemistry) A structure of a biological molecule in which there is a precise sequence or order of... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
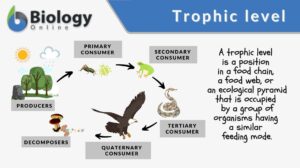
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
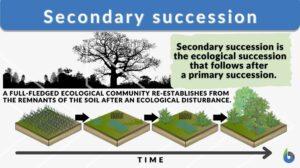
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Primary cell wall
Definition noun plural: primary cell walls ˈpɹaɪməɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms prior to... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Secondary structure
Definition noun A structure of a biological molecule characterized by the local folding within the biopolymer as a result... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Quaternary structure
Definition noun A structural level wherein several proteins (or polypeptide subunits) interact through non-covalent bonds to... Read More
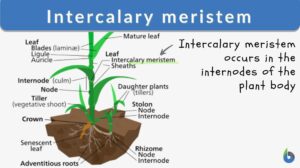
Intercalary meristem
The basic structural framework of plants is composed of different types of tissues. Based upon the capacity to divide, the... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Community (biology)
Community, in biology, refers to the assemblage of interacting organisms (either of the same or different species)... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More